Are you ready to travel anywhere on earth in less than an hour ?
Space exploration providers embrace the "Platform Revolution"
“That’s one small step for (a) man, one giant leap for mankind.”
Yes, it’s unforgettable. I find myself filled with a deep sense of longing, knowing that I missed the opportunity to witness the historic moon landing. It’s a moment of immense significance, and not being able to experience it firsthand leaves me with a sense of yearning for that pivotal chapter in history. The space bug did hit me in 1994, ever since I saw the magic of how a remote sensing satellite IRS-P2 was controlled remotely at ISRO Telemetry and Tracking (ISTRAC), Bangalore, India command center. This is the closest I have ever been to feel the historic moments in space exploration. While my professional journey took its turns, I have never given up on the hunger to continue to learn and rekindle the excitement with space and most importantly gain inspiration through the chaos in cosmos. Come join me to explore recent innovations in space industry.
“We choose to go to the moon in this decade and do the other things, not because they are easy, but because they are hard,”
JFK’s historic moon speech reshaped NASA’s direction.While we achieved significant milestones within a decade, our ambitions, such as lunar bases and Mars missions, often felt just out of grasp. We conquered the lower earth orbit, geostationary orbit and all these became part of the economic sphere of Earth. We could not include Moon to be part of this economic sphere through lunar base stations or tourism. It wasn’t a lack of national will; the main hurdle was the high cost of running a space program, making it tough to sustain within a national budget.
But, the last 10+ years have been the most exciting and memorable times. Thanks to a new breed of space enthusiasts, billionaires who are space nuts, I no longer have any regrets about missing the Apollo 11 moment. I am thrilled to be alive in this extraordinary space era of human history.
Jeff Bezos: “We get to preserve this unique gem of a planet by moving heavy industry off of Earth and Earth can be zoned residential and light industry. It’ll be a beautiful place to live, and we have to start now.”
Elon Musk: “I want to die on Mars. Just not on impact.”..“You want to wake up in the morning and think the future is going to be great — and that’s what being a spacefaring civilization is all about. It’s about believing in the future and thinking that the future will be better than the past. And I can’t think of anything more exciting than going out there and being among the stars.”…”The objective overall has been to make life multi-planetary and enable humanity to become a spacefaring civilization.” “Travel anywhere on earth in less than an hour”
Richard Branson: “We stand at the birth of a new industry that is going to lead to one of the biggest industrial revolutions in history. A revolution that will reshape our perception of space and how we utilize it for the benefit of humankind.”
I do dream their vision..Are we there yet ? It’s a journey for generations.
See this…a glimpse into Engineering marvel..
SpaceX is the reality..unlocking the space exploration industry. There are many “firsts”. Here are my favorites that gives goosebumps every time I realize this happened!
December 28th 2023 — SpaceX — Two orbital launches within 3 hours apart, shortest time between orbital launches at Cape Canaveral since 1966.
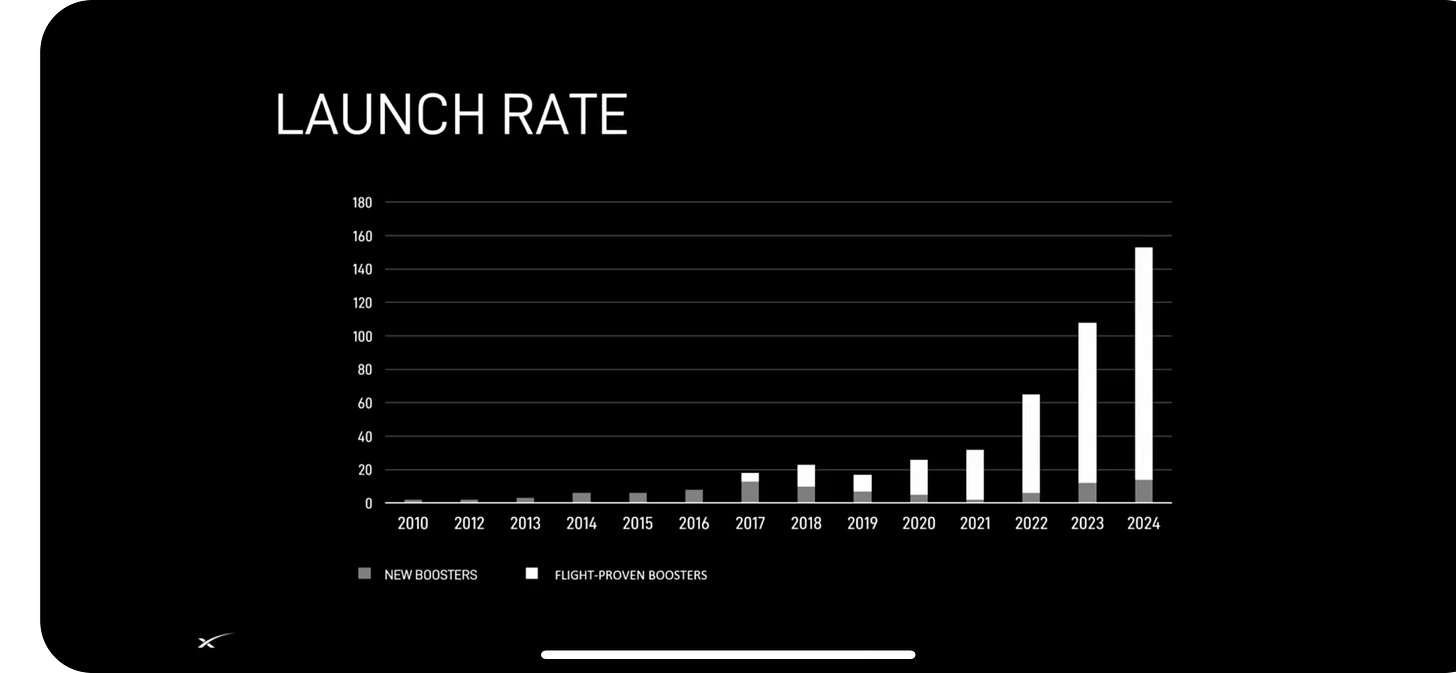
2023: SpaceX — Every 4 days there was a launch! 98 launches, including the 3 crew mission to ISS. Out of 223 Launch attempts globally, US had 109 attempts. 98 of these launches supplied by SpaceX. In 2022, SpaceX did 61 launches. Target for 2024 - 150 launches, 2.5 days per launch!
SpaceX Falcon Rockets — No other family of orbit-class rockets has ever flown more than 63 times in a year. Close to 2.6 Million Pounds of payload to the orbit!
SpaceX Starship First test flights in April/Nov 2023 — Transport vehicle to Mars and beyond! 400 Feet Tall, 17 Million pounds of thrust, 33 Raptor engines propelling up to 15K Miles per hour! Nothing comes close to this.
Falcon 9 Sticks the Landing (December 2015): SpaceX successfully landed its Falcon 9 rocket. And on Droneship. A critical step towards their goal of reusable rockets. On March 2017, reuses a rocket for first time
Falcon 9 first-stage boosters landed successfully in 261 of 272 attempts (96%), with 236 out of 240 (98.3%) for the Falcon 9 Block 5 version. A total of 234 re-flights of first stage boosters have all successfully launched their payloads.
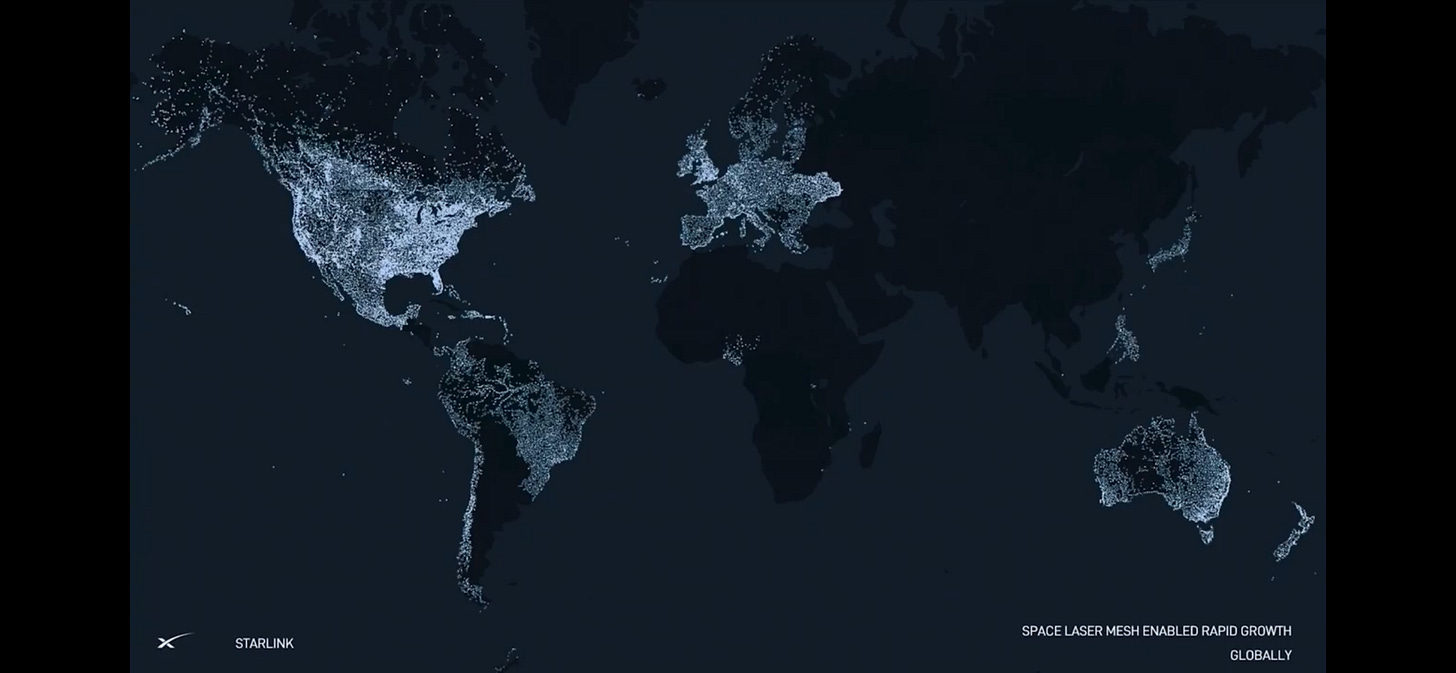
SpaceX enables close to 5000 Starlink Satellites in orbit part of SpaceX's Starlink broadband Internet network, 2.2Million subscribers worldwide. Jan 2024 - SpaceX has launched the first satellites with the capability to connect to smartphones on the ground with T-Mobile.
Why even have any buttons on Dragon Capsule for crew mission to ISS ? SpaceX innovative software centric fully autonomous capsule docking system with touch screen operations and control, all this is first ever.
The natural question that arises is
"How is SpaceX so successful - Business & Product sense?
I may not have all the qualifications to answer this question definitively, but I can certainly articulate why they stand out in terms of engineering excellence by aligning their practices with well-established guiding principles. SpaceX serves as a prime example of how these principles can be seamlessly applied and integrated, making them trailblazers in the realm of space exploration and innovation.
For every product and engineering systems out there, there is so much to learn just uncovering the mindset SpaceX has in adhering to these principles and being a role model to deliver disruptive innovations.
While one could write in depth on each of these principles, I wanted to share few key highlights on some of them:
Purpose Driven - SpaceX’s measurable “why” is so crystal clear with a journey fueled by a relentless sense of purpose. It would motivate anyone to be part of their mission. Their strategic approach and unwavering focus on execution enable the realization of this mission.
First Principles Thinking: SpaceX's groundbreaking success in rocket design and reusability, as seen in the Falcon 9 rocket, is a testament to their mastery of first principles thinking. They break down complex designs into fundamental components and reimagine them, optimizing for cost-efficiency while adhering to core principles.
Design Thinking Principles: User centric design & iterative prototyping is fundamental at SpaceX. For instance, the Dragon capsule exemplifies this approach with its touchscreen interface and automated docking/undocking capabilities. Why need button’s in the cockpit?
System Leadership Principles: SpaceX has been following holistic approach from rocket design to satellite networks to partnership ecosystems with NASA/others. With focus around outcome, it's able to innovate much faster than anyone.
Lean Startup Principles: SpaceX follows the build-measure-learn cycle by continually improving its rockets based on real-world data and testing. Starship 2nd launch while many considered failure, SpaceX celebrated this as it met the goals defined post 1st attempt failure.
Digital Transformation Principles: Digital Innovation at SpaceX leverages all digital technologies from rocket design, satellite communication and data analysis. Decision making is data-driven enabling efficiency and safety. For instance, telemetry is at the core of their operations, visible during live launches.
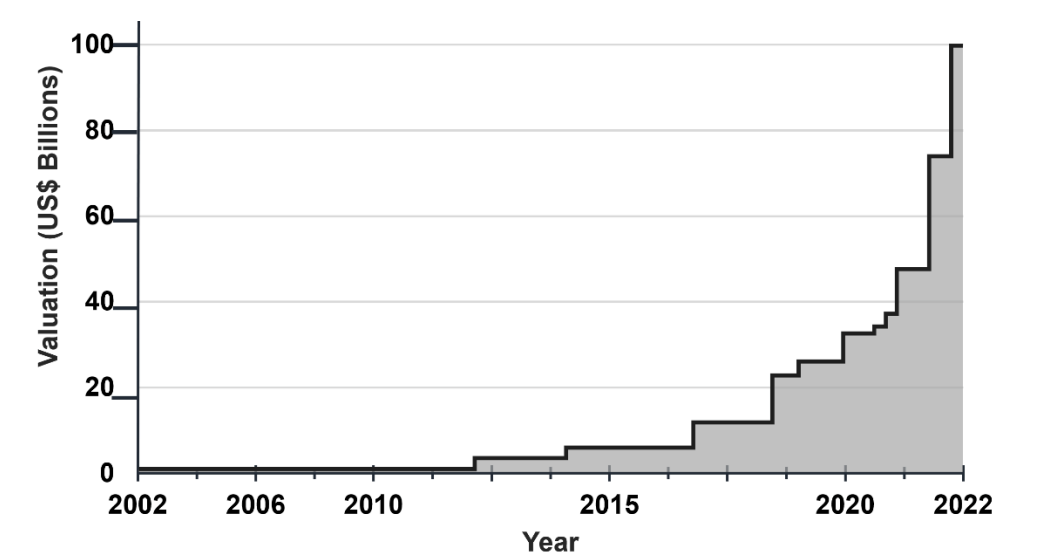
Now, beyond these engineering principles, it's fascinating to explore how SpaceX has emerged as a successful and valuable business, currently valued at $175 billion!! My exploration led to the following conclusions.
To understand this, we can view SpaceX not merely as a space exploration enterprise but as a technology company providing cutting-edge space exploration services. In today's business landscape, we've witnessed trillion-dollar market cap technology companies exemplifying a 'winner-takes-all' mentality through a “Platform strategy”. The platform economics has already demonstrated how services became faster, better, cheaper with scale. The successful emergence of platform players like Google, Amazon, Microsoft, Meta and few more were felt across the industry. Few notable trends were: Overall cost of the service came down, Rate of innovation increases, Addressable market expanded, Partner eco-system expanded.
SpaceX's triumph is not solely a result of the guiding principles discussed earlier, it is primarily driven by their skillful implementation of a Platform Strategy. Before exploring how SpaceX implemented this strategy, let’s explore their current success metrics as viewed through these lens: a) Cost to launch b) Service Agility - New Service expansion, Go-To-Market, Enabling partner eco-systems.
Cost to Launch:
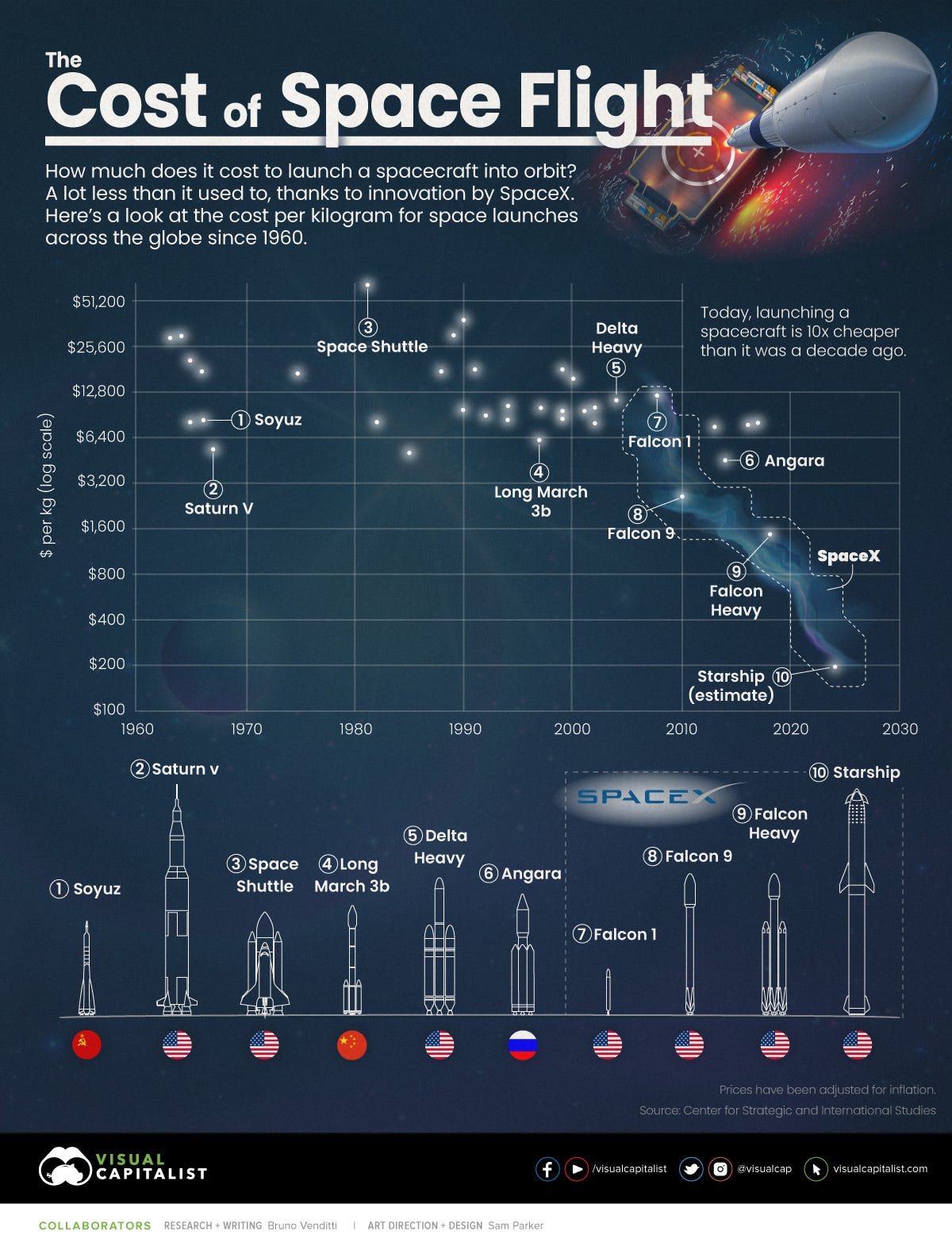
How much does it cost to launch spacecraft to carry payload to orbit ? Now, why these metrics are so important. NASA, enormous budget funded through tax payers is so positively influenced due to the innovations driven through SpaceX. The iterative innovative development with “fail fast” concept enabled SpaceX deliver reusable rockets. Reusability of rockets has changed all the economics. Again, the platform approach here includes leveraging Falcon 9 Rapid Reusable Reliable Rockets (4R) built on top of the learnings from Falcon1 and then extending the same to Falcon Heavy. Through efficient use of technology, rocket with fuel design and operational efficiency, cost to launch is drastically coming down. The most notable difference is SpaceX’s Vertical Integration approach - Build everything in house, deliver end to end, avoid overhead of supplier dependency and risk.
See the charts below articulating how SpaceX is transforming space exploration economics.
Industry metric : Cost per kg of payload to Lower Earth Orbit(LEO).
SpaceX : 2500$ via Falcon9, 1500$ via Falcon Heavy, estimated 100$ via Starship (leading to 10$).
In Contrast: 44 times cheaper than NASA Space shuttle.
SpaceX : Falcon 9 Development Cost including Falcon 9 Rocket ~ 390M$ and if the same rocket were to be built by NASA with the traditional development methods it would cost around 4B$.
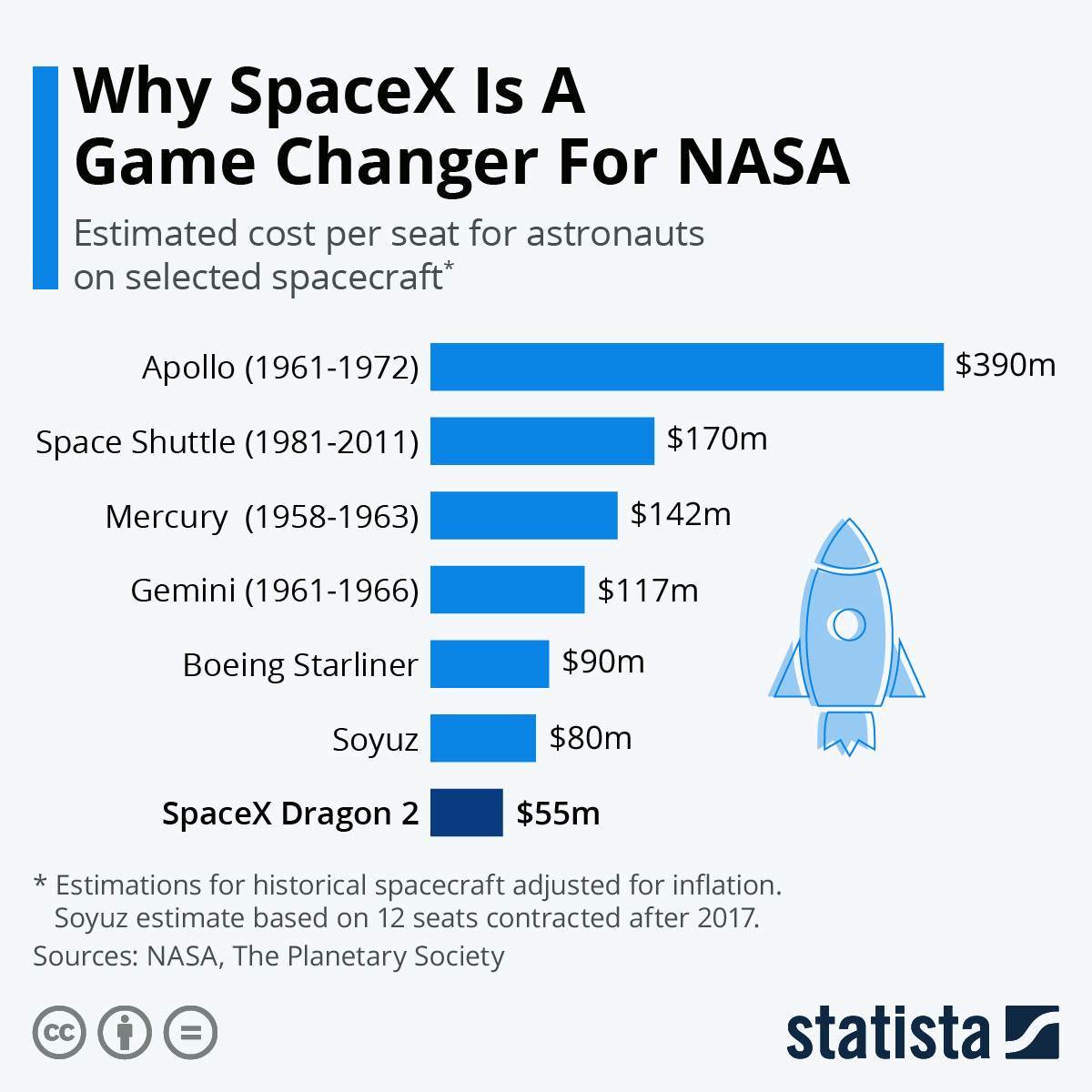
Another metric to look for is cost per seat for an astronaut to get a ride to ISS. NASA was paying $80M per astronaut in Soyuz, Russian shuttle to ISS.
Service Agility - New Service expansion, Go-To-Market, Enabling partner eco-systems:
SpaceX's extensive range of services and missions showcases its ability to cater to various space exploration and commercial spaceflight needs. A successful platform strategy demonstrates rapid expansion of capabilities once foundational building blocks are in place. The business goal is accomplished when you realize that ongoing innovation expenses are addressed through new service expansions. Secondly, when your platform enables flexibility to shift R&D expenses to next generation product from current product line without compromising customer outcomes. The fleet of services expanded at SpaceX dramatically when the foundational building blocks came together: Reusable with re-flight rocket technology stack, Dragon capsule readiness for crew missions with automated docking, and Starlink Constellation Network infrastructure.
The iterative development and delivery with new services is now paving the path for faster pace of launches, in-turn creating “S-Shape” growth anticipated with Platform delivery mindset.
Here is a snapshot of categories of service delivery with close collaboration with partners:
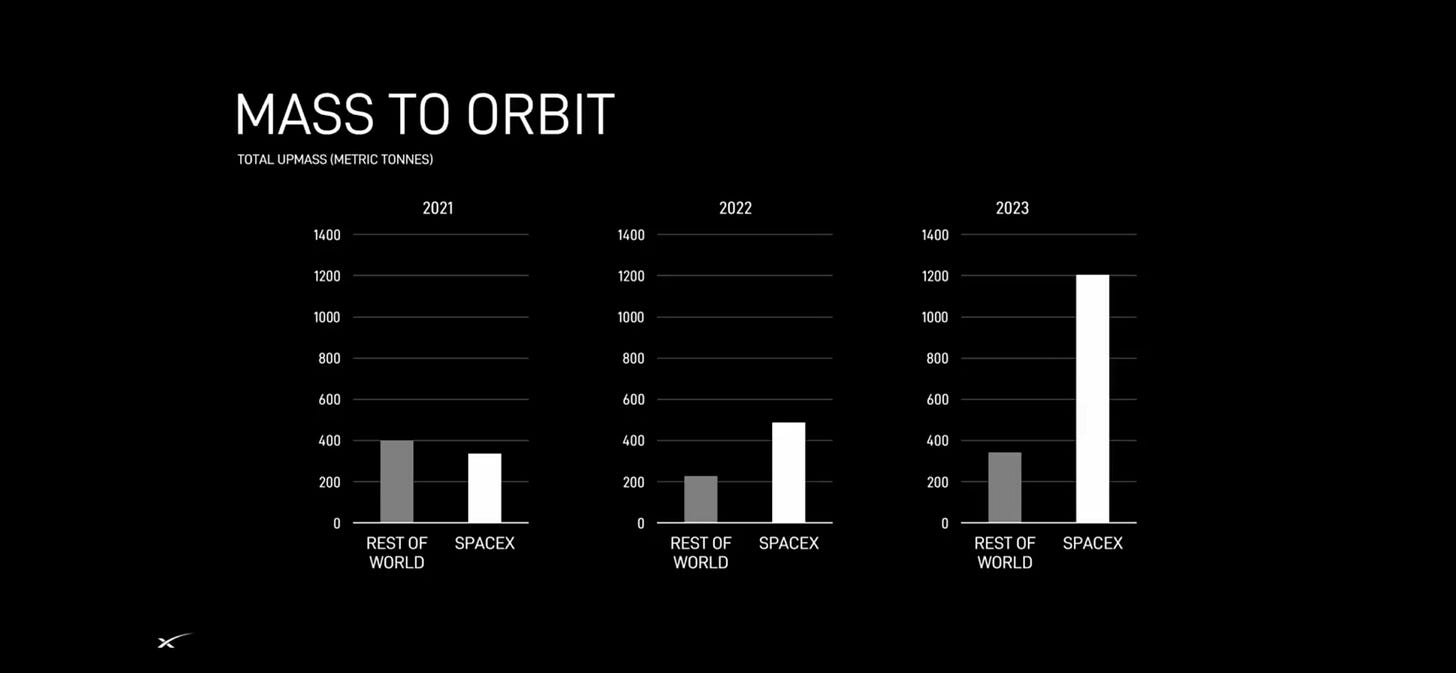
Orbital Payload Deliveries & Ride-share Missions: SpaceX has been actively delivering various types of payloads to orbit. This includes communication satellites, Earth observation satellites, and scientific research payloads, cargo to ISS. Below visualization articulates the power of SpaceX payload delivery. Through ride-share business model, SpaceX has demonstrated a great source of revenue stream.
International Space Station (ISS) Resupply Missions: Since May 2012, SpaceX's Dragon spacecraft has been a regular visitor to the ISS, delivering cargo and supplies. SpaceX's Dragon spacecraft is capable of carrying up to 6,000 kgs / 13,228 lbs of cargo to the Station and returning 3,000 kgs / 6,614 lbs of cargo back to Earth. To date, Dragon has made over 29 trips to the ISS.
Crewed Missions to ISS: In a significant achievement in May 2020, SpaceX restored human spaceflight to the United States by launching NASA astronauts to the ISS aboard the Crew Dragon spacecraft. This mission was notable as it was the first time a commercial spacecraft had carried astronauts to the ISS. As one could see the same Crew Dragon spacecraft has been designed to enable space tourism as another service extended to what enabled NASA missions.
Starlink Constellation - SpaceX offering broadband internet service leveraging the world’s largest constellation of highly advanced satellites operating in a low orbit around the Earth. These satellites delivered using the SpaceX Rocket and payload delivery framework. The unique differentiation of this service offering includes Internet on the Go (Boats, Hiking trips or any remote locations). This subscription service plan includes unlimited high-speed data with no long-term contracts or commitments. This service now extended with partnership with Telco providers like T-Mobile to offer Smartphone connectivity via the Starlink Satellite network.
Starshield - SpaceX delivers similar capabilities as Starlink but for Government entities addressing National security needs. It leverages the same platform stack by launching Starshield satellites, global communication network to government users and delivery of custom payloads as per government regulatory needs.
Credit: Internet Data
A Wall Street Journal report from August 2023 noted that SpaceX generated $1.5 billion in revenue during the year's first quarter and eked out a $55 million profit. That's a notable improvement for a company that posted annual losses over the past two years ($559 million on $4.6 billion of revenue in 2022 and a $968 million loss on half that revenue in 2021).
Meanwhile, Starlink is nearing profitability on a stand-alone basis. Musk reported that the company reached breakeven cash flow in late 2023. That business unit's revenue has surged six-fold over the past year to $1.4 billion.
As observed till date, SpaceX’s path to Platform execution strategy is through Fail-fast, Iterate, Measure, Learn and Improve. From Falcon1 first successful orbital flight to Starship, largest rocket ever leaving the pad, and crew missions to ISS and beyond, SpaceX is at the cusp of reaping the disproportionate value creation with growth of the platform. My immediate reaction to this tremendous value creation was attributed to increase in scale. But in any platform, including the one most of the digital economies operate on, the returns is usually seen when the appetite for learning and improve scales. As I further researched, came across great paper by Atif Ansar & Bent Flyvbjerg, who have articulated this concept extremely well. SpaceX’s approach has been around experimental learning:
From research paper: “Experimental learning is different from learning-by-doing or trial-and-error learning: “in experimental learning, variation in conditions is planned and intentionally introduced to produce insights about input output relations” typically about unknowns” Trial-and-error, in contrast takes place in “on-line” environments typically to refine ongoing knowns or regular activities.
SpaceX demonstrates “staircase” sequence learning as each experiment aids the next with crystal clear measurable outcomes. While it might look like a failure for external audience, SpaceX defines a clear outcomes for these experiments. Starship 2nd launch had headlines as failure while SpaceX celebrated success as it accomplished its defined outcomes.
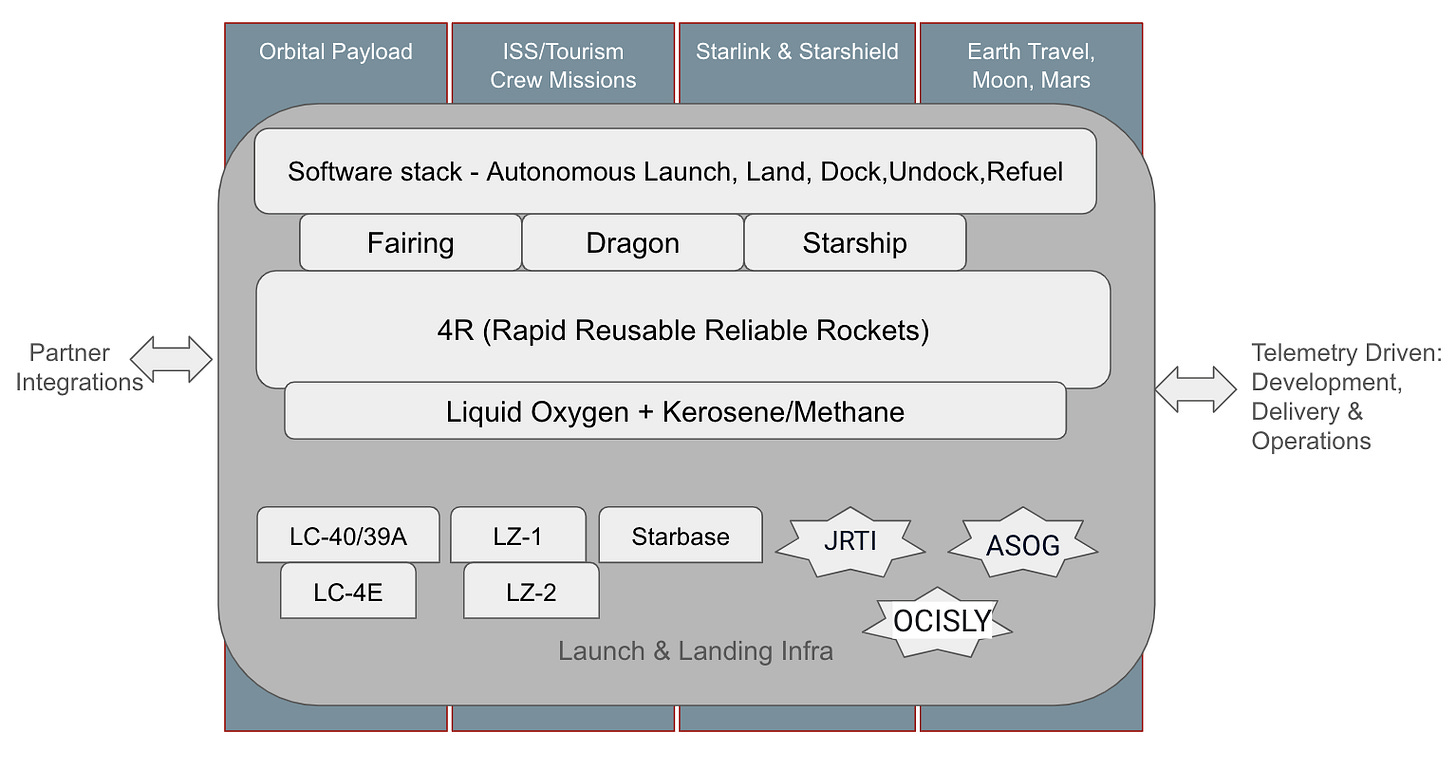
Now, I took the liberty to create a platform view for SpaceX with few of the building blocks as I understand. It’s an attempt on my part to map to a software as a service delivery platform stack. I am sure many of you would co-relate this architecture!
In summary, Space exploration industry is at the cusp of transformative disruption through innovations at SpaceX and others. Hard to predict what future holds but for sure it’s the most exciting times to see science fiction becoming reality as each event is the first milestone ever recorded in the history of mankind. I am fascinated and motivated by the flawless execution of what I think is the platform strategy at SpaceX.
Every day, I ponder the definition and SLA for any space exploration as a service readiness. SpaceX, post GA of their service offering, there has been 0 Customer Found Defect (CFD) while maintaining exponential growth in delivering the outcomes to their consumers.
While we could get ready with our Starport (aka passport) to travel anywhere on this planet within less than hour, it’s worth challenging ourselves in our own field..
What entails a 0 CFD platform? Thoughts..